In practice, how do we choose the correct screw?
June 08,2022
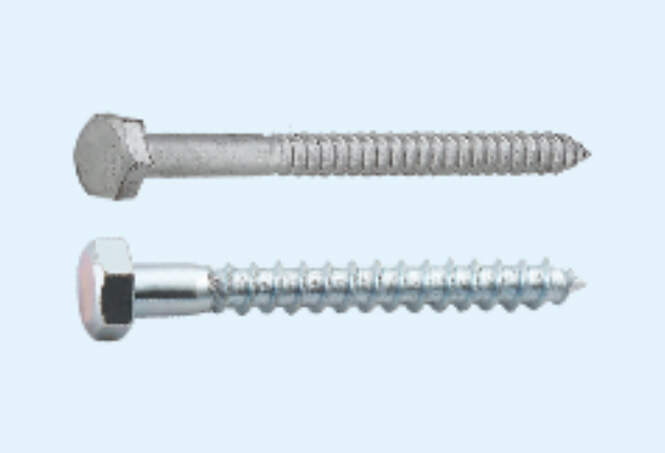
Square Head Chipboard Pozi Drive Funiture Screw
The difference between Square Head Chipboard Screw, Nut, Nut, Bolt, Screw, Stud: The standard saying is that there are no screws and nuts. Pozi Drive Future Screw is a common name, and those with external threads can be called "screw". The shape of the nut is usually hexagonal, and the inner hole is an inner thread, which is used to cooperate with the bolt and tighten the related parts.
The nut is a common name, and the standard should be called "nut". The head of the bolt is generally hexagonal, and the shank has external threads. The screw is small, the head has a flat head, a cross head, etc., and the stem has an external thread. The stud should actually be called a "double-ended stud", with external threads on both ends, and a polished rod in the middle. The long end of the thread is used to connect with the deep hole, and the short end is connected to the nut.
Definition of thread:
A thread is a shape with uniform helical protrusions on the outer or inner surface of a solid.
thread action
1. Fastening and connecting functions: suitable for most screw products at this stage.
2. Transmission effect (displacement effect): such as the micrometer used by QC to check the size.
3. Sealing function: such as the connection sealing of pipes.
Square Head Chipboard Screw Thread ·
A thread is a shape with uniform helical protrusions on the cross-section of the solid outer or inner surface. According to its structural characteristics and uses, it can be divided into three categories:
· Ordinary thread: the tooth shape is triangular, which is used to connect or fasten parts. Ordinary threads are divided into two types: coarse thread and fine thread according to the pitch, and the connection strength of fine thread is higher.
· Transmission thread: There are trapezoidal, rectangular, saw-shaped and triangular tooth shapes.
· Sealing thread: used for sealing connection, mainly pipe thread, tapered thread and tapered pipe thread.
Pozi Drive Funiture Screw thread fit grade Thread fit is the loose or tight size between screwed threads, and the fit grade is a specified combination of deviations and tolerances on internal and external threads.
1. For unified inch threads, there are three thread grades for external threads:
Grades 1A, 2A and 3A, there are three grades of internal threads: Grades 1B, 2B and 3B, all of which are clearance fits. The higher the rating number, the tighter the fit. In inch threads, the deviation is only specified for grades 1A and 2A, the deviation of grade 3A is zero, and the grade deviation of grades 1A and 2A is equal. The larger the number of levels, the smaller the tolerance.
· Class 1A and 1B, very loose tolerance classes, which are suitable for tolerance fits of internal and external threads.
· Grades 2A and 2B are the most common thread tolerance grades specified for inch series mechanical fasteners.
· Grades 3A and 3B, screwed to form the tightest fit, suitable for fasteners with tight tolerances, for safety-critical designs.
For external threads, grades 1A and 2A have a fit tolerance, grade 3A does not. The 1A tolerance is 50% larger than the 2A tolerance and 75% larger than the 3A tolerance. For the internal thread, the 2B tolerance is 30% larger than the 2A tolerance. Class 1B is 50% larger than class 2B and 75% larger than class 3B.
2. Metric thread, male thread has three thread grades:
4h, 6h and 6g, there are three thread grades for internal threads: 5H, 6H, 7H. (The Japanese standard thread accuracy grade is divided into three grades: I, II, and III, and is usually grade II.) In the metric thread, the basic deviation of H and h is zero.
The basic deviation of G is positive, and the basic deviation of e, f, and g is negative. H is a common tolerance zone position for internal threads, and is generally not used as a surface coating, or a very thin phosphating layer is used. The basic deviation of G position is used for special occasions, such as thicker coating, which is rarely used.
g is often used to coat a thin coating of 6-9um. For example, the product drawing requires a 6h bolt, and the thread before plating uses a 6g tolerance zone.
The thread fit is best combined into H/g, H/h or G/h. For bolts, nuts, Square Head Chipboard Screw, Pozi Drive Funiture Screw and other refined fastener threads, the standard recommends 6H/6g fit.
